Intro to Web Development With Python
Learning Objectives:
After this lesson, you will be able to:
- Describe how the web works.
- Explain what we mean by front-end and back-end.
- List the types of web developers.
Discussion: What’s the Web?
How do you think the web works?
Before we go about making a web app, let’s start with how the web works at all.
Finding a Florist
- How does a browser know what page to display?
Also known as:
- How do I call my florist? I can just call “Joe’s Florist” in my phone contacts.
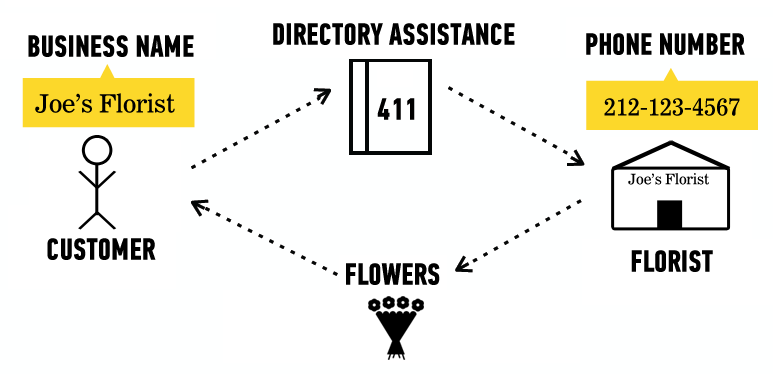
IP Addresses
- Website URLs — “Joe’s Florist”
- Just names to make our lives easier.
https://google.comhttps://reddit.com
- IP addresses — “515-115-5156”
- The actual address to which your browser goes.
Google.comis at172.217.12.142.reddit.comis at151.101.129.140.
Client-Server Relationship Review

In Real Terms
- Websites are just files your browser can read.
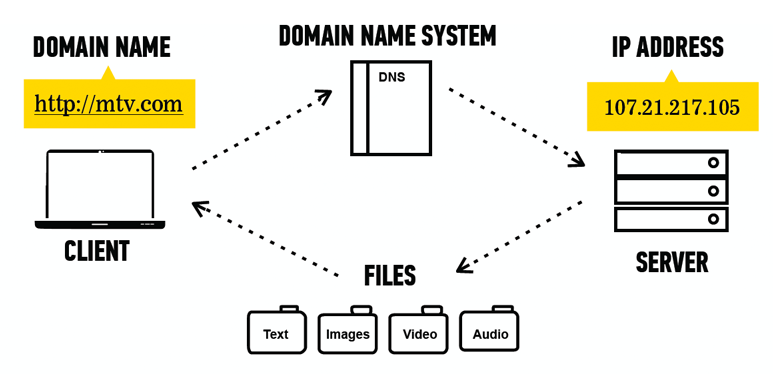
What Types of Files?
HTML (.html)
- Provides website structure.
CSS (.css)
- Adds colors and fonts.
JavaScript (.js)
- Makes the website interactive.
Images, text files, etc.
- Displays additional info on the webpage.
Quick Review
Where do websites exist?
- IP address: The actual location of a website on the internet.
Google.comis a friendly name for the IP address172.217.12.142, just like “Joe’s Florist” is a friendly name for the phone number “(515) 115-5156.”
How does a website work?
- Websites are actually just a bunch of files — images, text, and website-specific code.
- They’re hosted on servers — all the files for Google.com live on Google’s servers.
- Your browser is the client: It asks Google for the Google.com files so it can show them to you.
Discussion: What Is Web Development?
Does anyone want to guess (or know) what web development comprises?
Web
The work involved with building and maintaining a live website is split into two sides:
Front-End
- In a restaurant:
- The dining room.
- In web development:
- What the user sees.
Back-End
- In a restaurant:
- The kitchen, loading dock, and offices.
- In web development:
- What makes the website work (e.g., connects to servers).
- Behind-the-scenes code.
Front-End vs. Back-End: A Visual

Front-End vs. Back-End: A Better Visual

We Do: Front-End vs. Back-End
Head to the New York Public Library’s website: https://www.nypl.org/.
- What is the happening on the front-end?
- What is happening on the back-end?
Types of Web Developers:
Front-End Developer
- Languages used: HTML/CSS/JavaScript.
- Works on what the user sees.
Back-End Developer
- Languages used: Python, PHP, Ruby, or many others.
- Works on making the website work.
Full-Stack Developer
- Does both as well as database work!
Quick Recap
Front-end development:
- The visuals.
- How a website looks and how a user interacts with it.
Back-end development:
- The underlying code.
- How the website actually works.
Full-stack development:
- Includes both!
Discussion: What Is a Web Framework?
Does anyone want to guess (or know) what defines a web framework?
Web Framework
Web frameworks are used by both front- and back-end developers to make it easier to develop a website or web app.
Programming libraries:
- Are free for your use.
They make development far easier because they:
- Provide the client-server relationship piece.
- Add features to make it easier to write a large web app.
Frameworks are usually language-specific. Popular examples include:
- Flask, Django, React.js, Angular.js
Discussion: Web App vs. Website
Does anyone want to guess (or know) the difference?
Web App vs. Website
A website:
- Is typically informational.
- Has little-to-no interactive capabilities.
- e.g., The New York Times or a small company’s website.
A web app:
- Is an app hosted on the internet.
- Uses the client-server relationship to render a website.
- Offers the user more features than a static website.
- E.g., a bank’s webpage or an auction site.
You can have a hybrid!
- For example, a website can be static until the user logs in.
- Then, it’s a full-fledged web app.
Web Development Is Hard
- Don’t worry!
- GA has several classes dedicated to it (e.g., part-time Front-End Web Development or JavaScript Development, or the full-time Web Development Immersive).
- There’s a lot of information out there!
Right now, we’re going to be building web apps with Python!
Summary
What’d we do?
- DNS
- The actual address of a website.
- The Client-Server Relationship
- Server sends website files to the client (your browser).
- Front-End vs. Back-End
- What the user sees versus what makes the website work.
