---
## Learning Objectives
*After this lesson, you will be able to:*
- Write basic HTML.
- Write basic CSS.
- Style a Flask app.
---
## Customizing Our Flask App
Run your `my_website.py`. How does it look?
*Reminder: http://localhost:5000/*
How do we add colors? Styles? Formatting?
We need HTML and CSS.
> **Pro tip**: This is front-end web development!
---
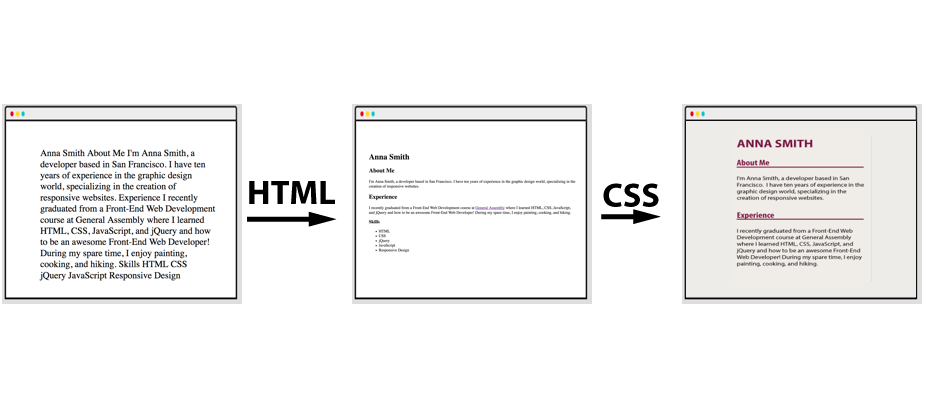
## HTML and CSS:
**HTML:** Content, Structure, and Presentation
- Paragraphs
- Headings
**CSS:** Style and Design
- Colors
- Fonts
---
## First, HTML
HTML means...
- Hypertext Markup Language
- HTML is **not** a programming language!
- Adding structure to a webpage. What's a heading? What's a paragraph? What's a list?

---
## HTML Elements
The fundamental building block of HTML is the element.
`
Here is a paragraph with p tags. The tags won't appear to the user.
`
- (Most) elements consist of:
- An opening tag (`
`).
- Indicates, "Format this content!"
- Defines what TYPE of content it is (e.g., paragraph, header).
- Content (e.g., text, images, video, or other elements).
- What the user sees.
- A closing tag (`
`).
- Indicates, "The content has ended."
- Has a `/`.
Tags are *always* in angle brackets.
---
## Types of Tags
Different tags apply different formatting.
- Paragraphs:
- These will be regular-sized text.

- Headings:
- These will be larger and bold text.

---
## Paragraph Tags

These are possibly the most common tags — all websites have paragraphs!
- Used to group related chunks of text.
- Browsers will apply default styling.
- The most universal content tag in HTML.
---
## Paragraph Tags
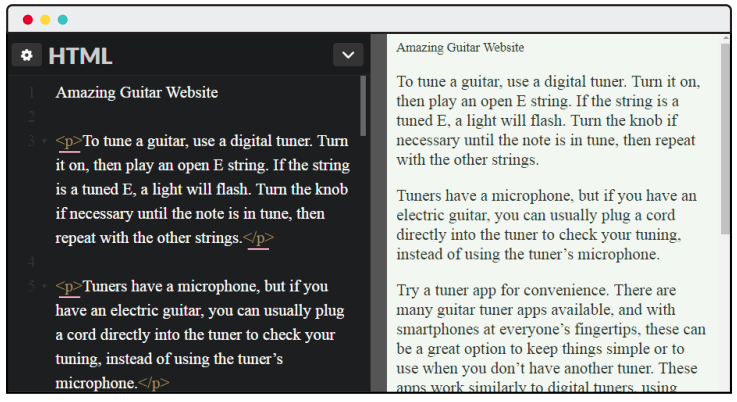
*Note: As "Amazing Guitar Website" doesn't have a `p` tag, it looks different. The browser doesn't yet know how to display it.*
---
## We Do: Paragraph Tags
Add `
` and `
` around the paragraphs.
- You might need to "Change View" to see both the input and output.
---
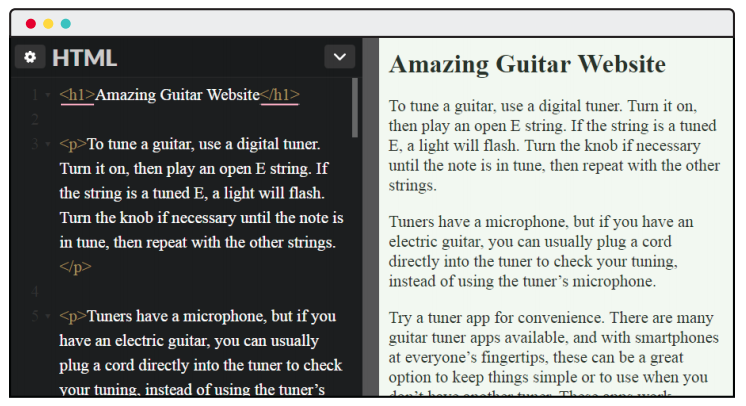
## Heading Tags

---
## Heading Tags
- Used to display text as a title/headline of a webpage or webpage section.
- Tags `
` through `
`.
- `
` defines the most important title on the page.
- Note that we didn't do anything — browsers just know headings are bigger!
---
## Heading Tag Sizing

---
## You Do: Heading Tags
- Put `
` around the paragraphs.
- Put `
` around `Anna Smith`.
- Put `
` around `About Me`.
- Put `
` around `Experience`.
---
## Heading Tags Solution
---
## What About Lists?
There are two types of lists:
- Unordered lists.
- Ordered lists (aka, numbered lists).

---
## The List Tag
- `
` defines an unordered list.
- Used together with list item: `
`.
```html
Chocolate
Strawberry
Vanilla
```
- Notice the indent — just like Python!
---
## Ordered Lists
- `` defines an ordered list.
- List item is the same: ``.
```html
Wake up
Brew coffee
Go to work
```
---
## You Do: Lists
- Set "Skills" to be an `h3`.
- Create an unordered list.
- Then create an ordered list!
---
## Lists Solution
---
## Quick Review
We've talked about HTML tags.
- They add structure to a page.
- Browsers automatically size paragraphs and headings appropriately.
- Lists are automatically given bullets or numbers.
All HTML is formed with tags:

---
## We Do: Defining HTML
1. Open any webpage.
2. Right click.
3. Click "View Page Source."
---
## HTML Structure: `doctype`
```html
```
- Short for "document type declaration."
- ALWAYS the first line of your HTML.
- Tells the browser we're using HTML5 (the latest version).
*Note: The CodePen did this automatically for us. It did a lot!*
---
## HTML Structure: ``
`` is the tag for HTML content!
- All HTML should be contained inside ``.
- Represents the root of your HTML document.
Within our `` tags, we have:
- ``
- ``
```html
```
---
## HTML Structure: ``
- ``: The first tag inside ``.
- Adds additional, behind-the-scenes content.
- Is not displayed, but is machine-parsable.
```html
< BEHIND THE SCENES HERE! >
< PAGE TITLE >
```
---
## HTML Structure: ``
- ``: The second tag inside ``.
- Follows ``.
- Contains HTML/content that **will** be displayed to the user.
- All other HTML will be placed here.
```html
Website Title
ALL HTML CONTENT GOES HERE!
Here's a paragraph with the p tag — this will actually get displayed.
Put whatever you want the user to see here!
```
---
## We Do: Create an HTML Doc
- Create a directory called `html_practice`.
- Create a file called `index.html`.
Put this content:
```html
Website Title
ALL HTML CONTENT GOES HERE!
```
Double click your file to open it in a browser!
---
## You Do: Create a Profile
Using the tags below, create a profile for yourself in your `index.html`.
Include: Name, About Me, and Hobbies.
**Put all your HTML and content in between the `` and `` tags.**
Common tags you might want to use:
- Paragraph: `
paragraph
`
- Heading: `
Welcome!
`
- Lists:
- Unordered (`
Things I like
`)
- Ordered (`1, 2, 3!`)
- List items (`
`)
- **Bonus:** Use bold (`bold`).
---
## Example Solution
```html
About Me!
Welcome!
I'm Sonyl and welcome to my profile!
Things I Like:
Animals
Food
Sleep
My Daily Routine:
Wake up
Drink coffee
Write great code!
Go to sleep
```
---
## Quick Recap
An HTML file looks like this:
```html
Website Title
< Everything the user sees goes here. >
```
This is the file your browser gets for any webpage you visit, like Google.com!
---
## Some Tags Need Attributes: Links
- What about… [a hyperlink that we want to click and go to another URL?](#)

- We need to tell the browser where the hyperlink should go.
```html
Clickable textClick here for Google.
```
**We Do:** Add a link to Google in your HTML. Reload!
---
## Some Tags Need Attributes: Images
- ``: A picture!
- But what picture? We need to tell the browser. The image needs a source: `src`.
```html
```
- Images are special — they have no closing tag!
**We Do:** Add this image in your HTML. Reload!
---
## Quick Recap
Some tags need more information: Where is the link going? What is the image? Give the browser whatever it needs to know.
Don't memorize these!
- There are hundreds of tags.
- You can always:
- Ask a friend.
- Ask me!
- Google "HTML" + what you want to do.
- E.g., "HTML image"
Up next: CSS!
---
## Styling: CSS
Let's switch gears. We have a structured website.
How do we style it?

---
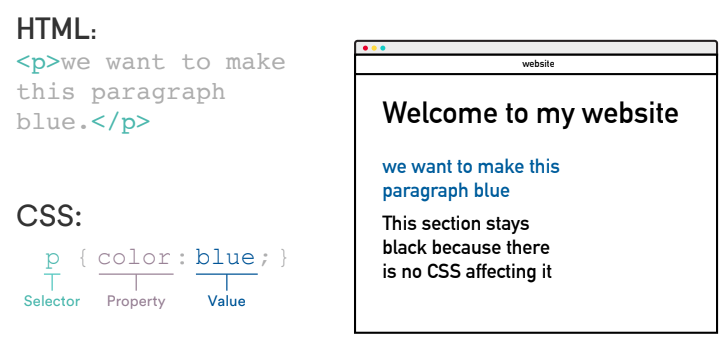
## CSS
CSS means…
- Cascading Style Sheets.
- Styling your HTML (e.g., colors, fonts, text sizes).
CSS tags match HTML tags.
- This rule turns everything with a paragraph tag (`
`) blue.
---
## CSS Color Property
You can set text color with `color`:
```css
p {
color: red;
}
```
Color values can be specified using:
- Color keyword (e.g., `red`).
- Hex code (e.g., `#FF0000`).
- The common way to set colors!
- Color-pickers online give you the code.
---
## We Do: CSS Color
In the CSS window, add:
```css
p {
color: blue;
}
```
---
## CSS: Syntax (CTN)
CSS font size:
- Sets the size of the font.
- We'll use pixel values (e.g., `12px`, `16px`).
Fun facts:
- One selector can have multiple declarations.
- It's common for each declaration to have its own line.

---
## You Do: CSS
In the CSS window, add:
```css
p {
color: blue;
font-size: 12px;
}
```
---
## Quick Review
We can now style elements. We can style any element with a tag!
```css
p {
color: blue;
font-size: 12px;
}
body {
color: yellow;
}
```
---
## Adding CSS to HTML
We have CSS. We need to tell the HTML about it! CodePen's been doing this for us.
- Like `
`, placed within `<head>` — it's something for the HTML to see, but not the user.
```html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Super Awesome Website
```
- `rel`
- Specifies the relationship between the current document and the linked document.
- `type`
- Specifies the media type of the linked document.
- `href`
- Specifies the location of the linked document.
---
## We Do: HTML With CSS
Let's do this.
- In the directory with your `index.html`, create `styles.css`.
- In it, put:
```css
p {
color: blue;
font-size: 12px;
}
body {
background: yellow;
}
```
- Save and reload!
---
## Quick Recap: HTML and CSS
HTML structures the page; CSS styles it. The CSS tags match the HTML tags.
We put CSS in a separate file and link it to the HTML.
```css
p {
color: blue;
}
```
```html
Super Awesome Website
Here's a paragraph the user will see — it will be blue!
```
This is a crash course. It's a huge topic! We just need the basics.
**Up next**: How do we do this with Flask?
---
## We Do: Adding HTML and CSS to Flask
Run your `my_website.py` — how does it look right now? Probably not the best…
*Reminder: http://localhost:5000/*
```python
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello_world():
return 'Hello, World!'
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)
```
Flask automatically makes the page structure for us — the `html`, `head`, `body`, `doctype`, etc.
**Discussion**: Where does that "return" go? Where could we put our HTML?
---
## We Do: Add Some HTML
Flask can have in-line styling and HTML right in the return!
- **Inside** the quotes. The `return` is what goes inside the `body` tag of the HTML.
Try this:
- Add italic tags around "Hello".
- Make the whole string an `h1`.
```python
def hello_world():
# Here,
# Add
return '
Hello, World!
'
```
What if we have a LOT of HTML?
---
## We Do: Add a LOT of HTML
Copy this code over:
```python
def hello_world():
line1 = "
Hello World!
"
line2 = "
If music be the food of love, play on!
"
line3 = ""
total = line1 + line2 + line3
return total
```
Do you think chaining lists is sustainable for a bigger webpage?
---
## Quick Recap:
Flask automatically makes a basic webpage for us. The HTML looks like this:
```html
Super Flask Website
< What we return in Flask goes here! >
```
Flask does that automatically — we just need to write the Python code for the `body`.
**Up next**: But what if we have a *ton* of code?
---
## We Do: External HTML File
Create a folder called `templates`.
- Flask always looks in a `templates` directory for HTML files.
Create a file called `index.html` with some HTML:
```html
Movie Search
Howdy!
```
---
## We Do: Tell Flask the HTML Exists!
How do we import an HTML file?
- `render.template`.
At the top of your file, add:
```python
from flask import Flask, render_template
```
In the `.py`, change your return to `return render_template("index.html")`.
- Save the lines you have! Just change the return.
Try it!
---
## We Do: Expanding the HTML
Now all our lines can go in the HTML:
```html
Hello World!
If music be the food of love, play on!
```
Try it!
---
## Quick Recap:
Flask automatically generates the webpage HTML and puts your HTML in the `body` tag — whatever you put in your `return` statement.
If your HTML gets to be too long to put in just a function without being confusing, you can make the HTML file yourself and tell Flask to load that.
---
## We Do: Adding CSS
`templates` folder:
- Where Flask looks for HTML files.
`static` folder:
- Where Flask looks for CSS files.
---
## We Do: Adding CSS
Create a `static` folder with a file, `style.css`.
Your directory should look like:
```
project_folder
│
│ │ my_website.py
│ │
│ │
│ └───templates
│ │ └─── index.html
│ │
│ │
│ └───static
│ └───style.css
```
---
## We Do: Background Color
Add this to `style.css`:
```css
body{
background: #FEDCBA;
font-family: "Times New Roman", serif.
}
h1 {
color: #012345;
}
```
What does it do? Reload your page!
What do you think happened?
---
## We Do: Importing the CSS
We have:
- HTML.
- CSS.
Flask knows about:
- The HTML.
What knows about the CSS?
What *should* know about the CSS? How can we do that?
---
## We Do: Putting CSS in the HTML
CSS styles HTML docs. We know that!
- As we saw earlier, the HTML doc needs to have the CSS link!
- In the HTML head, we need to have:
```html
```
The curly braces `{{ }}` call Flask!
- "Flask, find `style.css` in `static`."
**We Do**: Modify your `index.html`'s ``. Reload your page!
---
## Quick Recap
HTML structures pages. We can make a separate HTML file that Flask calls to load, in a `templates` folder.
CSS styles pages. We can make a separate CSS file in a `static` folder.
We have to tell the HTML file about the CSS file.
Flask calls the HTML file, which calls the CSS file.
---
## You Do: Customize Your Page
Modify your HTML and CSS files. Here are some ideas:
- Try changing the colors in your CSS file.
- Use `text-align` to `center` the content.
- Use `text-decoration` to `underline` the `h1`.
- Use other HTML tags! Can you make a hyperlink using `Click here `?
- Can you add a list using `
```
---
## Example CSS
```css
body {
background: #FEDCBA;
font-family: "Times New Roman", serif.
}
h1 {
color: #012345;
text-decoration: underline;
text-align: center;
}
```
---
## Summary
- HTML:
- Structures pages with headings, paragraphs, lists, etc.
- CSS:
- Styles pages! E.g., colors, bold, underline, font size.
- Adding HTML and CSS to Flask:
- Use the `template` and the `static` folders.
---
## Additional Reading
- [MDN Docs on CSS](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/)
- [MDN Docs on HTML](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML)
- [HTMLDog](http://www.htmldog.com/)
- [A Tutorial That Gets Into CSS Styling](https://code.tutsplus.com/tutorials/an-introduction-to-pythons-flask-framework--net-28822)
- [A Bullet List of HTML5 and CSS3 History](http://www.wdtonline.com/wdtMagazine/MemberWorks/WiserWays/csshtml.htm)