13 KiB
Intro to Data Science
Learning Objectives
After this lesson, you will be able to:
- Apply the data science workflow.
- Set up data science development ecosystem, specific to Python
What is Data Science?
-
The Harvard Business review called the industry the 'sexiest job of the 21st century'.
-
Glassdoor determined the profession to be among the most desirable in 2016 and 2017.
Sounds cool, right? But... what is it?
Data Science Examples
- Netflix recommendation engine.
- Apple FaceID determining if a photo contains your face.
- A bank approving a credit card.
Common thread:
- All leverage data to make decisions.
Class Question: What is an example of data science you have heard of? What about your stated example makes it be, well, data science?
Data Science Definition
Compliments of GA's Standard Board:
Data science is the practice of: acquiring, organizing, and delivering complex data; discovering relationships and anomalies among variables; building and deploying machine learning models; and synthesizing data to influence decision-making.
tl;dr: Data scientists:
- Use data of all kinds (numbers, text, images).
- Make explanations and predictive decisions.
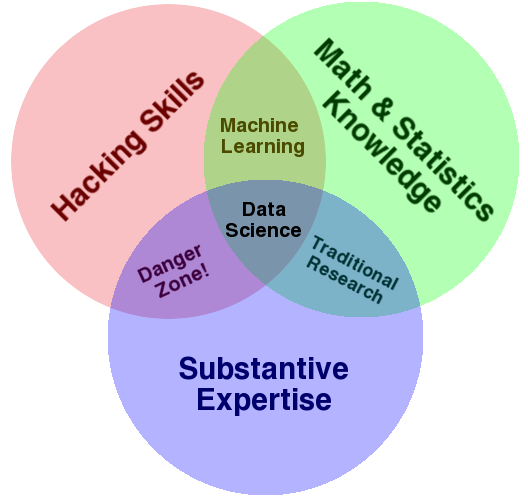
Conway Venn Diagram
- Note that data science lives at the intersection of computational skills ('hacking skills'), traditional statistics and mathematics skills, and subject matter expertise. A data scientist must be able to leverage maths/stats to develop models, computation skills to efficiently use those models, and subject matter competence to structure a problem and contextualize results.
Jobs in Data
What does that break down to?
- Machine Learning Engineer
- Data Scientist
- Data Engineer
- Research Scientist
- Data Analyst
Many of these jobs have some amount of overlap and are often used interchangably by companies. Make sure you read the job description to see exactly what is involved for a specific role!
How Do We...
- Go through data science workflow?
- Solve a data science problem?
- Craft a data science problem statement?
The Data Science Workflow
Class Discussion: Which step do you believe will be most challenging?
- There's no objectively correct answer!
Notes on the Steps
- Not hard-set rules.
- Really, problem-solving guidelines.
Every problem's different!
-
Some projects may not require every step.
-
It's normal to repeat certain steps a few times.
-
The process is cyclical with new findings!
The Data Science Workflow: Applied
You need to reduce the costs of staffing.
You have a table of DSW current retail sales associates across department stores.
The first three rows look like this:
| Job Level | Current Employee | Reason for Termination | Years of Service | Candidate Source | Previous Employer | School | Time to Fill (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Associate | N | New offer | 1.5 | Referral | Jake's Hawaiian Shirts | University of Minnesota | 40 |
| Associate | Y | N/A | 2.0 | Internship | N/A | University of Iowa | 15 |
| Associate | No | Tardiness | 0.5 | Online | Hats and Caps | University of Nebraska | 25 |
- Let's apply our workflow above to an interactive exercise. A given clothing retail company, Data Science Wearables (DSW), is interested in improving their human resource operations. Specifically, as a cost center in the business, this company wants to reduce their expenses associated with staffing the firm's in-store associates across the United States.
Data dictionary:
- Job Level: The role level. Our dataset is all current or former associates.
- Current Employee: If the individual is a current employee, this is a "Y" otherwise "N"
- Reason for Termination: If the employee no longer works at the retail store, this is why they left
- Years of Service: How long did the employee work at DSW?
- Candidate Source: Where did this employee learn of DSW?
- Previous Employer: Where did the employer previously work?
- School: Which university did the individual attend?
- Time to Fill (Days): How long did it take to fill this person's role? Typically minimizing time to fill is key to lower costs.
Step 1 is Always "Frame the Problem"
Solving data science task starts with a clearly defined problem.
- Poor results stem from no defined goal.
“A problem well stated is half solved.” — Charles Kettering
From there, you can apply your steps.
-
Even though all data science projects have different general flows, they start in the same place: with a problem. From this problem statement arises questions; questions we will ask the data in order to gain more information so we can attempt to find a solution to that problem.
-
Let's restate that: solving data science task starts with a clearly defined problem. Too often, situations will lack a driving objective. Haplessly exploring data without a determined goal produces poor results.
Step One: Frame
We know:
- We want to reduce costs associated with staffing.
Frame: Let's presume the key cost driver for this HR function is twofold: employees turning over early (low total years of service) and a high time to fill (positions going unfilled, costing producitivity losses). We'll aim to minimize turnover. Let's hypothesize we can explain how long an employee stays with the company based on their university, previous employment, and how they found our retail store, Data Science Wearables (DSW).
Step Two: Prepare
| Job Level | Current Employee | Reason for Termination | Years of Service | Candidate Source | Previous Employer | School | Time to Fill (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Associate | N | New offer | 1.5 | Referral | Jake's Hawaiian Shirts | University of Minnesota | 40 |
| Associate | Y | N/A | 2.0 | Internship | N/A | University of Iowa | 15 |
| Associate | No | Tardiness | 0.5 | Online | Hats and Caps | University of Nebraska | 25 |
Prepare: We would want to create a consistent data standard for Current Employee -> No to N across the dataset. Moreover, we need to hypothesize why NA values exist. E.g. did the second candidate not have a previous employer, or was this data unavailable? (We do not know with the information given.)
Step Three: Analyze
We want to:
- Create meaning and conduct statistical description and inference.
For example, the average Years of Service is ~1.33 years.
- Could we build a machine learning model to predict this?
- The data could center on their background (school, previous employers, and application source).
For example, is the relationship between Time to Fill and Years of Service positive or negative?
- Positive: when one increases, the other increases.
- Negative: when one increases, the other decreases.
Analyze: While we will dive deeper into analysis using Python soon enough, anecdotal evidence based on three observations seems to imply that Candidate Source is a useful explanatory variable. Employees that had experience with DSW previously (Internship and Referral) stayed longer. School does not seem to have useful signal for employee tenure, though it could with more data.
Step Four: Interpret
How do our results compare to our initial hypothesis?
What concrete actions do we recommend?
Interpret: It appears many of our explanatory factors helped, but not all, and not in ways we may have anticipated. School does not seem to yield valuable insight, but knowing an employee has been referred or had experience with DSW previously is a key signal. Perhaps DSW should expand their internship and employee referral programs.
Step Five: Communicate
Results are only as convincing as they are conveyed to key stakeholders!
Back up your statement with evidence, including statistical tests, visualizations, and model results.
Communicate: Our driving thesis is: The best candidates for DSW are those that have connected with the store in a previous way (internship, referral). Investing in these programs is recommended. Visualizations of average employee tenure segmented by these factors are encouraged.
Quick Review
The data science workflow:
Why Python for Data Science
Easy to write
- Data science is inherently a cross-functional discipline!
- A language for all audiences is key.
Open source
- New techniques become available daily!
- Developers from around the world race to implement new libraries.
- This places Python in contrast to closed source, paid data analysis tools like SAS and SPSS.
Often used for data analysis, scripting, and rapid software development.
Getting Data Science Tools
- We can analyze data to determine what Python is most used for:
- Pandas?
- A Python package for exploratory analysis.
- Let's use it!
Quick Review
-
Pandas
- A Python package for exploratory analysis.
-
Jupyter Notebooks and Jupyter Lab:
- The preferred integrated development environments (IDEs) of data science.
- We'll write our code in this!
Summary:
Data scientists:
- Use data of all kinds (numbers, text, images).
- Make explanations and predictive decisions.
Data Science Workflow:
- Frame -> Prepare -> Analyze -> Interpret -> Communicate.
Jupyter Notebooks:
- The industry tool!
- Interactive with Python.